What is Psoriasis ?
Share
What is Psoriasis and How Does It Affect the Skin?
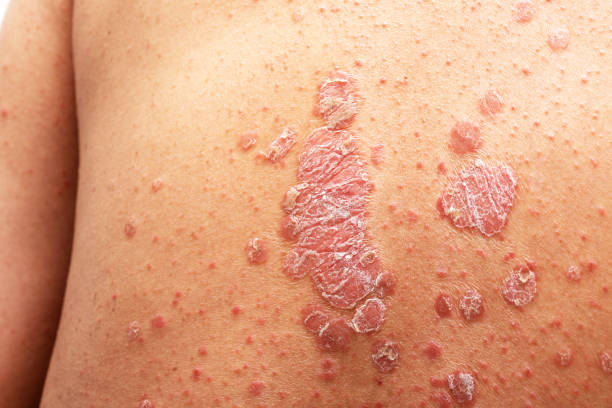
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition affecting about 2-4% of the global population. Psoriasis affects both males and females equally and can persist throughout a person's life. It causes a rash with itchy, scaly patches. These patches often appear on the knees, elbows, trunk, and scalp. Nail psoriasis, a manifestation of psoriasis, can cause irregular pits, onycholysis (lifting of the nail from the nail bed), proximal yellow bands, and nail plate splitting. It is commonly associated with plaque psoriasis.
At Psoriasis and Eczema Treatment Australia, we grasp the impact of psoriasis on skin cells. This leads to a buildup of dead cells on the skin’s surface. The risk of developing psoriatic arthritis, affecting about 30% of those with psoriasis, is also increased. Severe psoriasis can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
What is Psoriasis: Understanding the Basics
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease affecting millions globally. It’s caused by an overactive immune system, leading to skin cells multiplying at an alarming rate. This results in scaly patches, often in skin folds. The immune system, meant to protect us, attacks healthy skin cells in psoriasis sufferers.
There are various types of psoriasis, like guttate and pustular. Each type has unique symptoms. The National Psoriasis Foundation notes that 10%-30% of those with psoriasis also have psoriatic arthritis. This underscores the need for a holistic approach to treatment.
The Science Behind Psoriasis and the Immune System
Research has pinpointed over 80 genes linked to psoriasis. About 10 in 100 people carry genes that raise their risk. Smoking can nearly double the risk, and a family history significantly increases it.
Common Triggers and Risk Factors for Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis
-
Emotional stress: reported as a trigger for flare-ups in about 50% of individuals with psoriasis
-
Infections: such as streptococcal infections, are cited as triggers in around 10-15% of cases
-
Certain medications: like lithium and beta-blockers, are known to exacerbate psoriasis in approximately 5-10% of patients
Understanding psoriasis basics, including causes, symptoms, and risk factors, helps manage the condition. This improves overall quality of life for those affected.
Different Types of Psoriasis, Including Plaque Psoriasis, and Their Symptoms
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition affecting millions globally. It comes in various forms, each with distinct symptoms and characteristics. Plaque psoriasis, the most prevalent, accounts for 80% of cases. It manifests as thick, scaly patches that can be itchy and painful.
Other forms include guttate psoriasis, marked by small, dot-like lesions, and inverse psoriasis, featuring smooth, red patches in skin folds. Inverse psoriasis is often triggered by friction and sweating, prevalent in young adults. Symptoms vary by type and severity.
Some common types of psoriasis include:
-
Plaque psoriasis: characterized by thick, scaly patches
-
Guttate psoriasis: characterized by small, dot-like lesions
-
Inverse psoriasis: characterized by smooth, red patches in the skin folds
-
Pustular psoriasis: characterized by pus-filled bumps
-
Erythrodermic psoriasis: characterized by widespread, fiery skin
Understanding the different types of psoriasis and their symptoms is crucial for effective treatment. Recognizing each type's unique characteristics helps individuals with psoriasis and their healthcare providers. This collaboration is key to improving quality of life.
Symptoms and Complications
Psoriasis can manifest in a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild to severe. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in managing the condition effectively. Common symptoms of psoriasis include:
-
Red, scaly patches: These often appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. These patches can be itchy and uncomfortable.
-
Dry, cracked skin: The affected areas may become dry and cracked, sometimes leading to bleeding.
-
Itching, burning, or stinging: These sensations are common and can significantly impact daily life.
-
Thickening of the skin: Over time, the skin may become thicker in the affected areas.
-
Joint pain or stiffness: This can be a sign of psoriatic arthritis, a condition that affects about 30% of people with psoriasis.
In severe cases, psoriasis can lead to several complications, making it crucial to manage the condition proactively. Some of these complications include:
-
Psoriatic arthritis: This type of arthritis causes joint pain and stiffness, potentially leading to permanent joint damage if not treated.
-
Eye problems: Conditions such as conjunctivitis, blepharitis, and uveitis are more common in people with psoriasis.
-
Cardiovascular disease: Individuals with psoriasis are at a higher risk of developing heart disease, highlighting the need for comprehensive health management.
-
Depression: The emotional toll of living with psoriasis can lead to depression and anxiety, underscoring the importance of mental health support.
Understanding the symptoms and potential complications of psoriasis is vital for effective management. By recognizing these signs and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of further health issues.
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment
When symptoms of psoriasis appear, it's crucial to seek a doctor's opinion for a proper diagnosis. A diagnosis is usually made through a physical examination and a review of the patient's medical history. The doctor will look at the skin patches and assess the patient's overall health to gauge the condition's severity.
In some instances, a skin biopsy may be required to confirm the diagnosis. This involves taking a small skin sample for microscopic examination. Understanding the condition's severity is key to developing effective treatment plans. These plans may include topical treatments, such as creams and ointments, to foster healthy skin cells.
The treatment options depend on the condition's severity. For mild to moderate psoriasis, topical treatments are commonly used. In more severe cases, systemic medications or light therapy might be necessary. It's vital to collaborate with a healthcare provider to find the most suitable treatment for psoriasis and manage symptoms effectively.
Some common diagnostic methods include:
-
Physical examination
-
Medical history
-
Skin biopsy
By recognizing the symptoms of psoriasis and seeking medical attention, individuals can receive a proper diagnosis. They can then start treatment to manage their condition and promote healthy skin cells.
Treatment Options Available in Australia
Treating psoriasis involves various methods and approaches to alleviate symptoms and prevent heart disease. In Australia, a variety of treatments exist, from topical creams to systemic drugs and phototherapy. About 3 out of 10 psoriasis sufferers also develop psoriatic arthritis, making tailored treatment plans crucial.
Knowing the different psoriasis types, like plaque psoriasis, which affects 9 out of 10, is vital. Identifying triggers like stress and certain drugs can help manage symptoms better.
Topical Treatments and Systemic Medications
Topical treatments, like creams, are used for mild to moderate psoriasis. They reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth. For severe cases, systemic medications like methotrexate and cyclosporin are prescribed. These can lower inflammation and prevent joint damage.
Phototherapy and Natural Remedies
Phototherapy, using ultraviolet light, is effective for psoriasis. Natural remedies, such as aloe vera and tea tree oil, may also help. It's important for individuals to work with their healthcare provider to create a personalized treatment plan.
By exploring treatment options and consulting with healthcare professionals, people with psoriasis can manage their condition. This approach helps reduce the risk of heart disease and other related health issues.
Conclusion: Living Well with Psoriasis
Though there's no cure for psoriasis, managing it and living well is achievable. At Psoriasis and Eczema Treatment Australia, we know psoriasis can be tough and ongoing. Yet, with the right treatments and lifestyle changes, people can manage their health and enhance their life quality.
Effective treatments like topical therapies, phototherapy, and systemic medications can lessen symptoms. These include silvery scales and thin plaques on the skin. A healthy lifestyle, stress management, and monitoring for comorbidities also help prevent flare-ups. This reduces the risk of conditions like pus-filled lesions.
Our clinic is dedicated to creating personalized treatment plans and support for psoriasis patients. By working with our dermatologists and healthcare team, individuals can develop a management strategy that meets their needs. This empowers them to actively manage their skin health.
