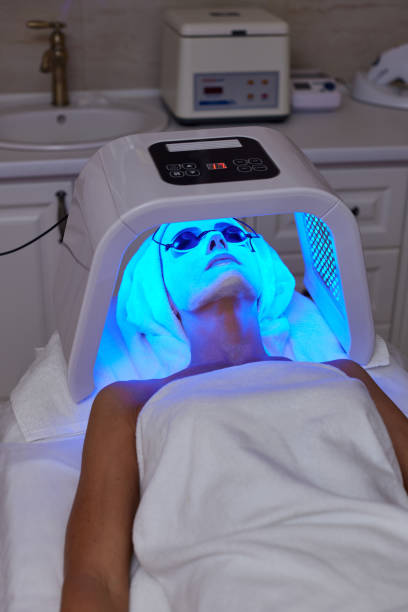
Psoriasis Light Therapy and Vitamin D: The Science Explained
Share
Understanding the connection between sunlight, vitamin D, and skin conditions is crucial in psoriasis treatment. Since the early 1900s, ultraviolet radiation has been used to manage psoriasis. Today, vitamin D is a key focus, with the Office of Dietary Supplements recommending 600 IU daily for most adults.
Research indicates that people with psoriasis often have low vitamin D levels. This is due to limited sun exposure or a poor diet. Cod liver oil and trout are natural sources, but caution is advised. Exceeding 4,000 IU daily can be harmful. A 2022 study found that high-dose vitamin D3 (30,000–60,000 IU) may reduce symptoms. Yet, side effects like kidney stones are possible.
Light therapy, such as Narrowband UVB, has shown significant results. A 2017 study revealed that 75% of patients experienced improvement with regular sessions. Australian Psoriasis and Eczema Supplies offers guidance on combining light therapy and vitamin D strategies for healthier skin. PUVA therapy, while effective, requires medical monitoring to avoid risks like skin cancer.
Understanding Psoriasis and Its Relationship with Vitamin D
Psoriasis symptoms occur when the immune system mistakenly speeds up skin cell growth. This leads to patches, with plaque psoriasis being the most common, affecting 80–90% of cases. Other forms include guttate psoriasis (small red dots), nail psoriasis (pitting), and scalp psoriasis (scaly patches). These conditions make the skin dry, prone to irritation, and susceptible to flares caused by stress or infections.
At Australian Psoriasis and Eczema Supplies, we understand that healthy skin depends on vitamin D. It plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses and skin cell growth. Vitamin D helps control keratinocyte maturation, reducing inflammation and excessive cell buildup. Deficiencies can worsen psoriasis flares by disrupting these processes.
-
Low vitamin D levels are common in psoriasis patients, with those having darker skin tones synthesising less vitamin D from sunlight.
-
Vitamin D analogues in topical treatments like creams slow skin cell overgrowth, easing plaques without the drawbacks of steroid creams like thinning skin.
-
Deficiencies may heighten psoriasis severity by impairing immune regulation and skin barrier function.
Managing vitamin D levels is crucial for systemic health and the effectiveness of topical therapy. Australian guidelines suggest 600–800 IU daily through diet, supplements, or sunlight. Foods like salmon (477 IU/3 oz) or fortified milk (115–130 IU/cup) can be beneficial, though topical treatments are often the mainstay of therapy.
|
Psoriasis Type |
Affected Areas |
Key Triggers |
|---|---|---|
|
Plaque Psoriasis |
Elbows, knees, scalp |
Cold weather, stress |
|
Guttate |
Trunk, limbs |
Bacterial infections |
|
Nail |
Fingernails/toenails |
Injuries, fungal infections |
|
Scalp |
Scalp area |
Scratching, tight headwear |
For those managing psoriasis, balancing vitamin D intake with topical therapies like coal tar or systemic treatments can improve outcomes. Our products utilise vitamin D analogs to help reduce psoriasis symptoms safely. Always consult a healthcare provider before adjusting treatments.
How Psoriasis Light Therapy Works
Psoriasis light therapy employs ultraviolet light to combat skin cell overgrowth and inflammation. UVB light, a crucial element, decelerates skin cell proliferation by targeting DNA in rapidly dividing cells. This intervention halts the cycle leading to thick, scaly patches. Australian Psoriasis and Eczema Supplies explains how this treatment strikes a balance between healing and safety for those affected areas.
The Science Behind Ultraviolet Light and Skin Cells
UVB light slows skin cell growth by disrupting DNA in keratinocytes, halting their rapid reproduction. This action reduces inflammation and enhances affected areas. Narrowband UVB phototherapy employs precise 311-313nm wavelengths, proving effective with fewer side effects than older UVB treatments. For severe cases, excimer laser therapy delivers targeted ultraviolet rays directly to plaques, preserving healthy skin.
Why Light Therapy Can Slow Skin Cell Growth and Reduce Inflammation
Light therapy operates through three primary mechanisms:
-
UVB triggers apoptosis in overactive immune cells, calming inflammation
-
UVA combined with psoralen (PUVA) enhances skin penetration but carries higher long-term cancer risk
-
Vitamin D production from UV exposure aids in reducing redness and scaling
Skin specialists advocate for narrowband UVB as the first-line treatment due to its safety profile. Pulsed dye lasers target blood vessels feeding psoriasis plaques, offering another option for stubborn lesions.
Types of Light Therapy and Their Effects
Common approaches include:
-
Narrowband UVB: 50-90% see improvement with 3 weekly sessions over months
-
PUVA: More effective for severe cases but requires careful monitoring
-
Excimer laser: Ideal for localized plaques like scalp or hands
Australian guidelines suggest limiting PUVA to under 150 sessions to mitigate skin cancer risks. Regular skin checks are advised for all patients undergoing prolonged uvb therapy.
Types of Light Therapy Treatments for Psoriasis
Light therapy offers flexible options for managing psoriasis, with Australian Psoriasis and Eczema Supplies providing access to leading treatments like narrowband UVB and home UVB phototherapy systems. These therapies use ultraviolet light to slow skin cell overgrowth and reduce inflammation. Here’s how each method works:
A bright, well-lit laboratory setting showcasing various types of light therapy devices for psoriasis treatment. In the foreground, a selection of phototherapy lamps, including UVB narrowband, UVA, and excimer laser units, neatly arranged on a clean, white countertop. In the middle ground, a human model undergoing a light therapy session, their skin exposed to the therapeutic rays. The background features diagnostic equipment, shelves of medical supplies, and large windows allowing natural daylight to fill the space, creating a serene, professional atmosphere. The overall scene conveys the scientific and clinical nature of light-based therapies for managing psoriasis.
-
Narrowband UVB: This is the most common form of UVB treatment. It uses specific wavelengths (311-313nm) to treat large skin areas. Sessions typically occur 2–3 times weekly, gradually increasing exposure time. It’s safer and more effective than broadband UVB.
-
Excimer Laser: Delivers targetted ultraviolet to small, stubborn plaques like those on the scalp or knees. This precision reduces the number of treatment sessions needed compared to traditional phototherapy.
-
Pulsed Dye Laser: Focuses on blood vessels beneath plaques, easing redness and thickness. This artificial light therapy avoids harming healthy skin while addressing inflammation.
-
Home UVB Phototherapy: Home systems let patients follow a consistent treatment schedule in the comfort of their home. Australian Psoriasis and Eczema Supplies offers devices for at-home use, but proper training and medical guidance ensure safe results.
-
Natural Sunlight: Moderate natural sunlight exposure can aid mild cases. Yet, artificial light from clinics offers controlled dosing to avoid sunburn and long-term skin damage risks.
Excimer laser therapy often requires fewer treatments than traditional UVB sessions due to its high precision. Home phototherapy treatments from Australian Psoriasis and Eczema Supplies let users maintain consistent care without frequent clinic visits. Always consult a dermatologist to select the best approach, balancing effectiveness with safety.
Benefits and Risks of Light Therapy for Psoriasis Patients
Light therapy provides options for psoriasis patients, but it's crucial to weigh its benefits against potential risks. Australian Psoriasis and Eczema Supplies notes that UVB therapy is effective for treating moderate to severe cases. It shows up to 90% response rates for plaque and guttate psoriasis. Yet, managing risks like skin cancer and irritation is essential.
An airy, sun-drenched room with a large window overlooking a lush garden. In the foreground, a patient sits calmly in a specialized light therapy booth, the bright UV rays gently caressing their skin. The middle ground features a physician discussing treatment options, pointing to a diagram illustrating the benefits of light therapy for psoriasis, such as reducing inflammation and stimulating vitamin D production. In the background, shelves hold medical journals and samples of various light therapy devices. The scene conveys a sense of hope, expertise, and the balanced consideration of both the advantages and potential risks of this effective psoriasis treatment.
Effectiveness for Different Types of Psoriasis
UVB therapy is effective for:
-
Plaque psoriasis: 50-90% improvement after 15-20 sessions
-
Scalp psoriasis: Specialized combs target hard-to reach areas
-
Nail psoriasis: Excimer lasers address stubborn nail bed lesions
Understanding the Risk of Skin Cancer
|
Treatment Type |
Effectiveness |
Cancer Risk |
|---|---|---|
|
Narrowband UVB |
High |
Low (minimal skin cancer link) |
|
PUVA (UVA + psoralen) |
Strong for widespread psoriasis |
High (melanoma risk over time) |
Australian guidelines suggest regular skin checks for all patients, but this is more critical for those with fair skin or a history of UV exposure. It's important to avoid tanning beds, as their uncontrolled UV radiation is dangerous.
Combining Light Therapy with Other Treatments
Combination therapy enhances outcomes:
-
Topical vitamin D analogues applied before UVB boost cell regulation
-
Oral retinoids paired with UVB reduce needed light exposure
-
Coal tar or salicylic acid prep skin for better penetration
Australian Psoriasis and Eczema Supplies advises consulting a skin specialist. They can tailor combinations, such as topical corticosteroids with UVB, for sensitive areas.
Conclusion: Integrating Light Therapy into Your Psoriasis Management Plan
Managing psoriasis demands a customised strategy, with light therapy being a vital component. UVB phototherapy, backed by over a century of research, shows significant success, with a 70% improvement rate for many. Combining it with topical or systemic treatments can enhance results and reduce dependence on a single method. Begin by consulting your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable phototherapy for your condition's severity.
Adherence to a regular treatment schedule is crucial. UVB sessions, typically 2–3 times a week for 6 weeks, often lead to noticeable symptom reduction within weeks. Australian Psoriasis and Eczema Supplies provides essential tools like moisturisers and cleansers, as advised by the National Psoriasis Foundation. Integrating these with phototherapy ensures a comprehensive approach, addressing skin health and vitamin D pathways essential for skin cell regulation.
While UVB has fewer systemic side effects than PUVA, it's important to always protect your skin from the sun and undergo regular skin checks. For severe cases, biologics might be needed, but UVB is a cost-effective initial choice. By combining light therapy with lifestyle changes and medical advice, you can develop a plan for long-term remission and improved skin appearance. Effective treatment hinges on consistency and teamwork with your healthcare team—start managing psoriasis with evidence-based methods today.
FAQ
What is psoriasis light therapy?
Psoriasis light therapy, or phototherapy, employs ultraviolet (UV) light to combat the overactive immune response and excessive skin cell production in psoriasis. It aids in managing symptoms such as scaling and inflammation.
How does vitamin D affect psoriasis?
Vitamin D is vital for skin health, regulating skin cell growth and maintaining the skin's immune system. It helps slow down the excessive skin cell production in psoriasis. This is why vitamin D analogues are often used in treatments.
Can light therapy increase the risk of skin cancer?
There is a risk of developing skin cancer with prolonged UV exposure. Yet, modern light therapy techniques like narrowband UVB pose a significantly lower risk compared to older methods. Adherence to treatment protocols and careful monitoring help minimize this risk.
How often should I undergo light therapy for psoriasis?
Treatments typically involve sessions 2-3 times weekly. The frequency can vary based on individual needs and the severity of psoriasis. It's crucial to follow the treatment plan set by your healthcare provider.
Is home UVB phototherapy effective?
Yes, home UVB phototherapy can be effective for many individuals, offering the convenience of consistent treatment schedules. Yet, proper training and medical supervision are essential for safety and effectiveness.
What are the factors to consider before starting light therapy?
Considerations include the severity of psoriasis, personal health history, current medications, and geographic accessibility to treatment facilities. A thorough discussion with your skin specialist is essential to tailor the best treatment approach for you.
Are there specific types of psoriasis where light therapy is more effective?
Yes, light therapy is more effective for plaque psoriasis and guttate psoriasis. Patients with moderate to severe psoriasis covering significant body areas often experience more benefits from phototherapy compared to milder cases.
Can I combine light therapy with other psoriasis treatments?
Absolutely! Combining light therapy with topical treatments, like vitamin D analogues or corticosteroids, often enhances treatment effectiveness and may lead to quicker results.
What should I do if I experience skin irritation after light therapy?
It's common to experience some skin irritation following light therapy. If the irritation persists or worsens, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider to adjust your treatment plan as needed.

1 comment
Hello, I was wondering if you could help me. I am considering purchasing your products. Could you guide me and tell me the difference between the dermalight and Desktop lamp?
I am looking on supporting someone with Psoriasis in the body and scalp.
thank you in advance,
Siuling